Bitcoin Myths
Breaking down the most common Bitcoin misconceptions.
Bitcoin, a revolutionary technology, elicits diverse reactions from individuals around the world. While nearly everyone has heard of Bitcoin, very few have devoted the necessary time to fully comprehend its intricacies. Consequently, Bitcoin has become one of the most misunderstood technologies of our time. In this article, I delve into prevalent misconceptions surrounding Bitcoin and examine their veracity.
Bitcoin is a Ponzi scheme
According to the US Securities and Exchange Commission:
“A Ponzi scheme is an investment fraud that pays existing investors with funds collected from new investors. Ponzi scheme organizers often promise to invest your money and generate high returns with little or no risk. But in many Ponzi schemes, the fraudsters do not invest the money. Instead, they use it to pay those who invested earlier and may keep some for themselves.
With little or no legitimate earnings, Ponzi schemes require a constant flow of new money to survive. When it becomes hard to recruit new investors, or when large numbers of existing investors cash out, these schemes tend to collapse.”
Ponzi schemes tend to exhibit common characteristics, such as promised high returns, low risk, involvement of unlicensed sellers, unregistered investments, secretive strategies, issues with paperwork, and difficulties in receiving payments.
Upon careful analysis of this definition, it becomes apparent that Bitcoin does not fit the characteristics of a Ponzi scheme. There are several key factors that distinguish Bitcoin from such fraudulent schemes. To begin, there is no promise of high returns or minimal risk when investing in Bitcoin. As with any investment, Bitcoin carries inherent risks, and the potential for high returns is accompanied by the possibility of financial loss.
Additionally, Bitcoin operates as an open-source protocol, ensuring accessibility and transparency of its code to all participants. Unlike Ponzi schemes that rely on secrecy to obfuscate their fraud, Bitcoin's distributed and open nature encourages scrutiny and analysis. In this way, Bitcoin stands in stark contrast to a Ponzi scheme since it is a distributed software accessible and verifiable by everyone.
Finally, Bitcoin functions as a protocol governed by its users, with no founding members reaping benefits from new investors. There was no initial distribution of bitcoins among insiders. From the moment the first Bitcoin block was mined in January 2009, anyone, anywhere had the freedom to mine Bitcoin and obtain some coins for themselves. This fair and inclusive launch contradicts the notion of a Ponzi scheme which favours insiders.
By understanding these significant distinctions, it becomes clear that Bitcoin's characteristics and operational model do not align with that of a Ponzi scheme.
Bitcoin is too volatile to function as money
“Volatility is a symptom that people have no idea of the underlying value”
-Jeremy Grantham
One common misconception about Bitcoin is that it is too volatile to function as money. The term volatility refers to the rapid and unpredictable fluctuations in the price of Bitcoin, which can make it challenging to use for everyday transactions. However, it is crucial to note that volatility is not an intrinsic characteristic of Bitcoin as a technology but rather a reflection of its relatively young and evolving nature.
Volatility is a natural aspect of price discovery as an asset undergoes monetization. Considering no one alive today has witnessed the real time monetization of any good, it is understandable that some individuals are hesitant about Bitcoin's volatility.
As more individuals and institutions adopt Bitcoin and participate in its market, the increased liquidity and growing investor base will contribute to the maturation of Bitcoin as an asset and can decrease its volatility. As such, it is not unreasonable to expect Bitcoin’s volatility to decrease over time.
This expectation aligns with historical evidence, as Bitcoin's 14-year existence has witnessed a significant decrease in volatility from its earliest days. When examining The Bitcoin Volatility Index, a noticeable decline in Bitcoin’s volatility over time is evident.
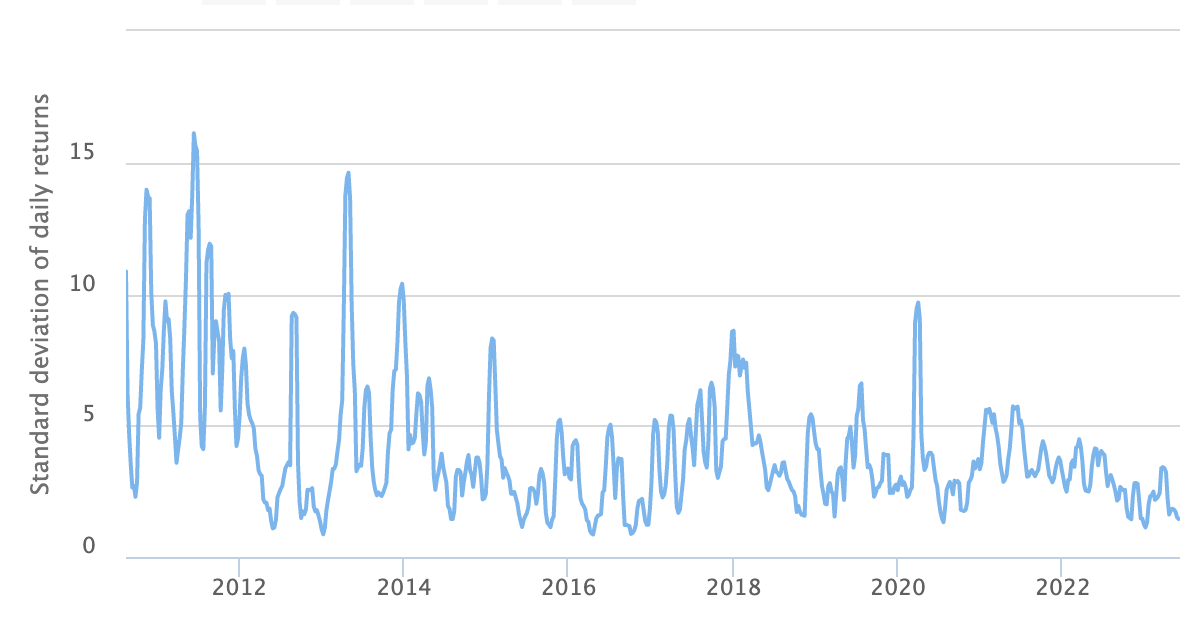
It is also important to note that Bitcoin’s volatility is more accurately characterized as upward volatility. Despite strong price fluctuations in either direction, the long-term trend of Bitcoin’s price has consistently moved upward throughout its entire existence. This upward trajectory highlights the underlying strength and resilience of the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin has no intrinsic value
Value is not intrinsic, it is not in things. It is within us; it is the way in which man reacts to the conditions of his environment.
-Ludwig Von Mises
Another common misconception about Bitcoin is that it lacks intrinsic value. Intrinsic value refers to the inherent worth of an asset, often associated with its tangible qualities or underlying assets backing it. Critics argue that since Bitcoin is digital without physical form and it is not “backed” by anything, it cannot possess intrinsic value.
However, it is essential to recognize that intrinsic value can take on many forms. Bitcoin derives its value from being an open, permissionless, and decentralized monetary network. Combined with its robust security, its functionality as a store of value, and its vast network effects, the value of Bitcoin becomes clear.
Bitcoin's decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks, and provides individuals with direct control over their money. This feature resonates with those seeking financial autonomy and security. Additionally, Bitcoin's limited supply, set at 21 million coins, ensures scarcity, which is a fundamental driver of value in economics.
Furthermore, Bitcoin's utility as a medium of exchange and store of value contributes to its worth. As more businesses accept Bitcoin and more users hold it as a long-term investment, its practicality and usefulness will continue to grow. The expanding network effect, where the value of a network increases as more participants join, further solidifies Bitcoin's intrinsic value.
While Bitcoin's value may be intangible in the physical sense, it possesses real-world utility and derives its worth from a combination of technological innovation, network effects, and the trust and confidence bestowed upon it by its users. It is this collective belief and adoption that underpin Bitcoin's intrinsic value, challenging the misconception that it lacks a solid foundation.
Bitcoin is bad for the environment
One of the main criticisms leveled at Bitcoin is its energy usage. While the implications surrounding Bitcoin and the environment are complex enough to span an entire article (stay tuned…) I will address some of the key points here.
Firstly, the percentage of global energy consumed by Bitcoin is relatively small, estimated at around 0.1%. This makes it trivial why so much attention is focused on its environmental impact. The reality is, Bitcoin could disappear tomorrow and we would be no closer to solving any of our environmental problems.
It is also worth noting that Bitcoin mining is an entirely electric process, meaning there are no direct emissions associated with mining Bitcoin. Similar to electric vehicles, the emissions intensity of Bitcoin mining depends on the source of the electricity used.
Research from Daniel Batten, a climate VC, shows that over the last 3 years alone, the emissions intensity of the Bitcoin network has fallen over 50% due to an increasing usage of sustainable energy sources. This highlights the magnificence of the free-market economics that underpin Bitcoin.
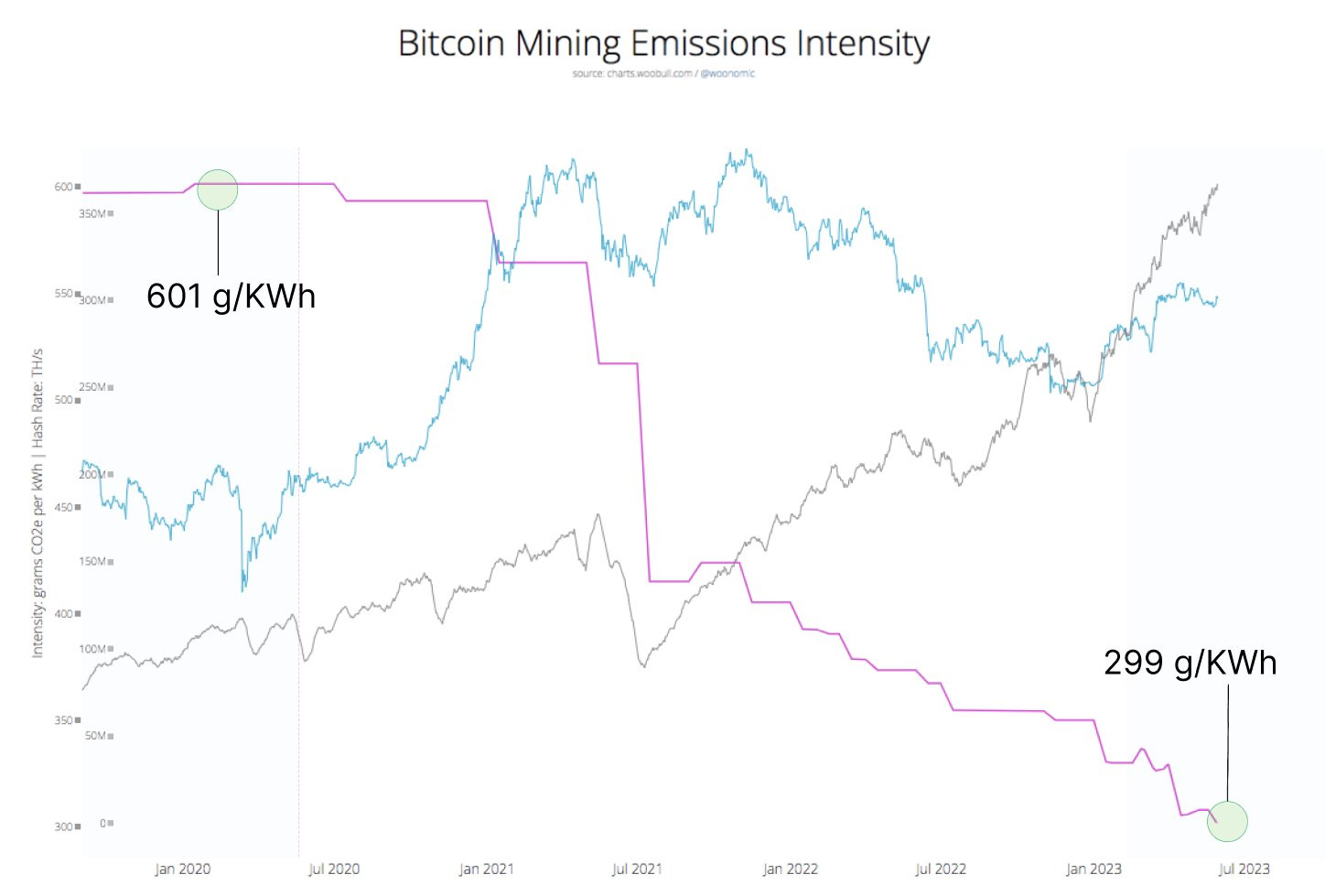
This reduction in emissions intensity stems from the fact that a majority of Bitcoin mining is powered by sustainable energy, making it one of the cleanest industries on the planet. Further research conducted by Daniel Batten suggests that 52.6% of all mining is being done sustainably. Data from the Bitcoin Mining Council suggest this figure may be even higher, reaching nearly 60% of all mining being done sustainably. These figures demonstrate that, even in the absence of regulatory requirements, there is a free market incentive for Bitcoin miners to use sustainable energy.

To further solidify this point, its important to understand that the competitive nature of Bitcoin mining necessitates access to low-cost energy, which often comes in the form of renewables or wasted energy sources like flared gas and methane leaking from landfills. In most cases, fossil fuels are simply too expensive. By making use of these otherwise wasted energy resources, Bitcoin mining can even have a carbon-negative impact. This further enhances the sustainability of the network and contributes to mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
Bitcoin miners are also non-rivalrous consumers of energy, meaning they do not compete directly with the energy used in our day-to-day lives. This is because the electricity we use in our daily lives is too expensive to profitably mine Bitcoin. Instead, miners will often tap into excess renewable energy during periods of low demand or utilize stranded energy sources that would otherwise go to waste. This synergistic relationship between Bitcoin mining and renewable energy helps promote the adoption and development of cleaner energy infrastructure now and in the future.
Finally, it is essential to acknowledge the environmental impact of the traditional financial system and industries like gold mining. The banking sector has significant ties to the fossil fuel industry, with billions of dollars invested in it. These investments directly support and sustain environmentally harmful practices. Furthermore, gold mining involves the destruction of our ecosystems to extract the raw mineral. It would be much more constructive to scrutinize these industries rather than Bitcoin.
A stunning example of this can be seen with the big five banks in Canada, namely TD, BMO, RBC, CIBC, and Scotiabank. Since the signing of the Paris Climate Agreement in 2015, these financial institutions have invested over $910 billion in the fossil fuel industry. As a result, they find themselves among the top 20 financiers of fossil fuels globally. It is clear that these banks are directly providing support to the fossil fuel industry. By keeping your money within these institutions, you inadvertently contribute to the continued operation and expansion of environmentally damaging practices.
In contrast, Bitcoin offers a compelling alternative—a bank in cyberspace backed by a majority of sustainable energy. By holding your money in Bitcoin, you actively support the use of sustainable energy and contribute to reducing emissions resulting from harmful environmental practices. This shift in financial choice allows individuals to align their economic activities with their environmental values, empowering them to make a positive impact.
In summary, it is imperative to look beyond the framing of Bitcoin mining as a black and white issue and consider it within the broader context of the world. Bitcoin mining is increasingly powered by sustainable energy, and the network's energy consumption is relatively small compared to traditional financial systems and industries. Bitcoin's synergistic relationship with renewable energy can drive its adoption, innovation, and reduce emissions from wasteful practices. Additionally, the traditional financial system, including major banks, has significant ties to the fossil fuel industry, making Bitcoin a much more sustainable alternative.
Bitcoin is anonymous and only used for illicit activities
Many people mistakenly believe that Bitcoin transactions are anonymous, making it the ideal tool for illicit activities. However, this overlooks key aspects of how Bitcoin operates, such as its pseudonymous nature and the immutability of its blockchain. Bitcoin transactions can be more accurately described as pseudonymous rather than anonymous, this is similar to how an email address does not reveal personal details but serves as a custom identifier.
While it is still challenging to directly associate a Bitcoin transaction with a specific individual, additional investigative techniques can be employed to uncover the identities behind Bitcoin addresses. As such, the transparent nature of the blockchain makes it possible to trace the flow of funds and detect patterns of suspicious behaviour.
The second feature that renders Bitcoin undesirable for illicit activities is the immutability of the blockchain. The Bitcoin blockchain is a ledger containing the entire history of Bitcoin transactions. This not only makes it difficult for criminals to conceal their activities, but also enables law enforcement agencies to analyze and track illicit transactions over time.
These characteristics of Bitcoin make it undesirable for illicit use. In reality, fiat cash is often the preferred medium for illicit activities as it provides a higher level of anonymity and is more challenging to trace. Consequently, a significantly larger amount of illicit activity occurs using traditional currencies like the US Dollar rather than Bitcoin. In fact, the share of illicit transactions from all cryptocurrencies was just 0.34%. In contrast, up to 5% of all cash transactions may be involved in illicit activities.
Bitcoin will be hacked or shut down
Bitcoin stands as an impenetrable fortress in the digital realm, representing the most robust computer network on the planet. This is due to the security granted by the underlying technology of blockchain as well as the immense amount of computational power backing the Bitcoin network.
“The blockchain itself is economically and technically impervious to corruption.”
-River Financial
Bitcoin has been operating securely since its inception in 2009, with no successful hacking attempts on the core protocol. Bitcoin transactions are secured using advanced cryptographic algorithms, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to tamper with or manipulate transaction data.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network adds an additional layer of security. This distributed consensus mechanism makes it highly resistant to hacking attempts, as any malicious activity would require control over a majority of the network's computing power, which is currently considered practically infeasible.
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin also dispels the notion that it could be shutdown. This is because there is no central authority or single point of failure that can be targeted or shut down. Each node in the network maintains a copy of the blockchain, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance.
Even if some nodes are taken offline, the network continues to function and validate transactions through the remaining nodes. In the face of regulatory pressures or attempted disruptions, the distributed and resilient nature of the network ensures its continued operation and the preservation of its core principles of security and trust.
The Bitcoin network's unwavering commitment to security, anchored by its sophisticated cryptographic design and decentralized consensus mechanism, has solidified its reputation as a trustworthy protocol. This high level of security exhibited by Bitcoin instills confidence in individuals and firms, ensuring their monetary value is safeguarded. This robust security framework positions Bitcoin as a viable monetary system capable of serving the entire world, fostering trust, and enabling global financial transactions with unparalleled peace of mind.
Bitcoin is a bubble
Last but not least, we address the popular notion that Bitcoin is nothing more than a speculative bubble waiting to burst. Many will draw false comparisons between Bitcoin and the Tulip Mania that occurred near the end of the Dutch Golden Age between 1634-1637. However, this false attribution overlooks Bitcoin’s underlying technology and growing adoption.
The notion of a bubble implies that the value of an asset is artificially inflated and detached from its intrinsic worth. Unlike traditional financial bubbles, Bitcoin derives its value from its utility as a decentralized digital currency and store of value. This in turn gives Bitcoin intrinsic value and makes it a powerful financial tool with real world use cases.
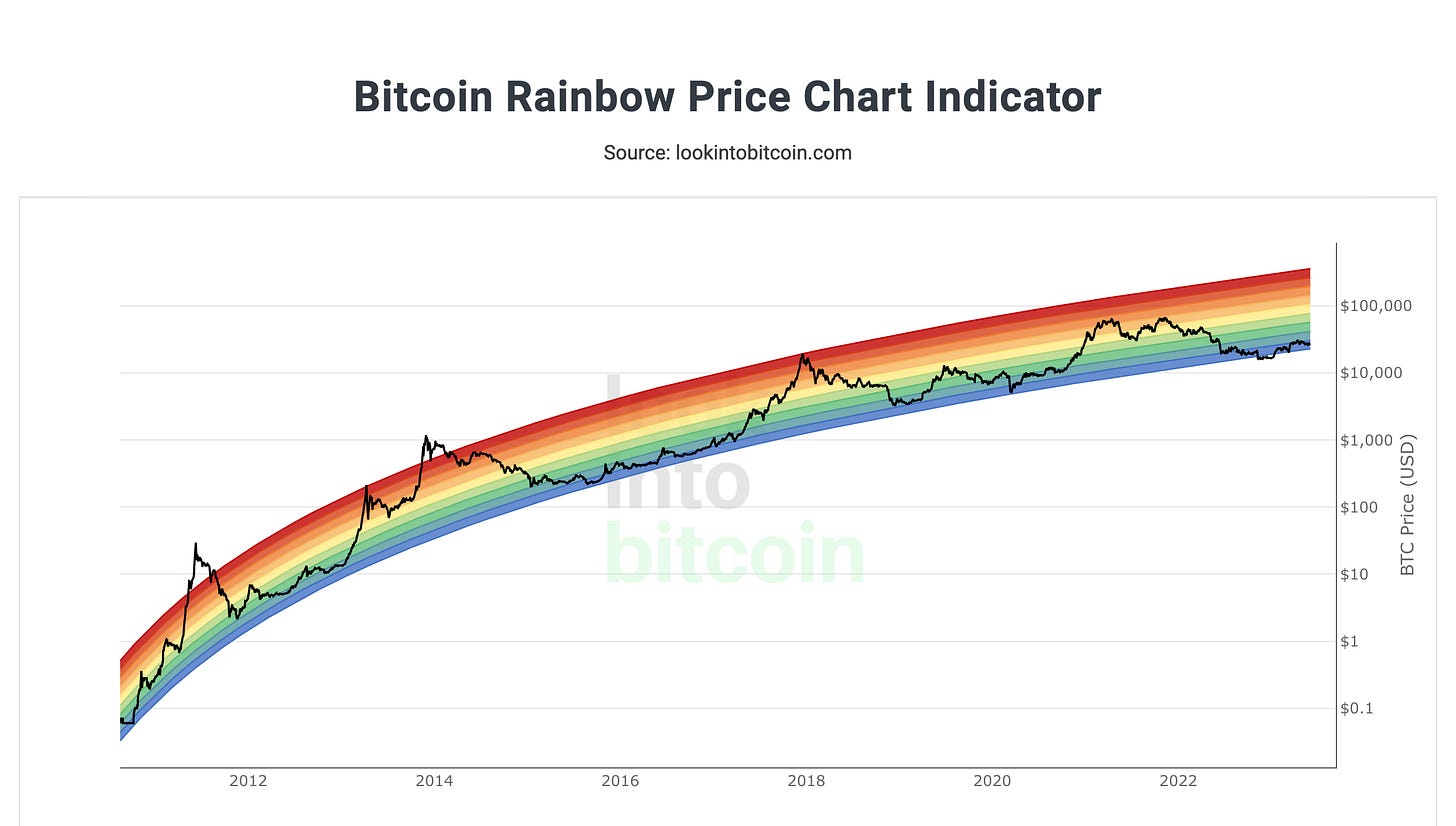
Furthermore, the growth and adoption of Bitcoin have followed a distinct trajectory, marked by periods of volatility and price corrections. These fluctuations are typical of any emerging asset class undergoing price discovery. While short-term price swings may give the impression of a bubble, zooming out and examining the long-term trend reveals Bitcoin's consistent upward trajectory. Moreover, Bitcoin's market capitalization and liquidity have significantly increased over time, indicating a broadening investor base and a more mature market.
While Bitcoin has experienced price corrections and market cycles, it has consistently recovered and reached new all-time highs. This resilience and ability to bounce back from market downturns highlight the underlying strength and growing acceptance of Bitcoin as a legitimate asset class. Labeling Bitcoin as a bubble oversimplifies its complex dynamics and fails to consider its utility, growing adoption, and underlying technology.
Final thoughts
This article aimed to highlight prevalent misconceptions about Bitcoin by providing some key facts about this emerging monetary network. We clarified that Bitcoin’s operational model and characteristics do not align with that of a Ponzi Scheme. By functioning as an open, decentralized currency, with absolute scarcity we established that Bitcoin does have intrinsic value despite its digital nature.
Next, we established that Bitcoin is a leader in the adoption of renewable energy and can play a key role in advancing the adoption of clean energy as well as having a carbon negative impact. Furthermore, while Bitcoin remains volatile during its current phase of price discovery, it is projected that over time this volatility is likely to decrease as adoption grows and the market matures.
We emphasized how the decentralized nature and advanced security model of Bitcoin makes it impervious to hacks or shut-downs. We also showcased the inherently anti-illicit nature of transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. Finally, we addressed the notion that Bitcoin is a bubble, clarifying that this claim oversimplifies the complex dynamics and growing adoption of Bitcoin.
By understanding these prevalent misconceptions and gaining a deeper understanding of the truth behind Bitcoin, individuals and firms are empowered to make more informed decisions regarding this transformative technology. Whether it's embracing its decentralized nature, acknowledging its intrinsic value, or understanding its role in renewable energy adoption, dispelling these myths opens up a world of possibilities. By recognizing Bitcoin's true potential, individuals and firms can position themselves at the forefront of innovation and help pave the way toward a more prosperous future.



Well done!
Nice!!!!